Frequently asked questions About Patterns of Strengths and Weaknesses (PSW)
Answers by Milton J. Dehn, Ed.D.
What is PSW?
PSW is a method for identifying students with specific learning disabilities. It is one of three methods allowed under Federal learning disability legislation.
Which federal and state legislation is PSW based on?
;
The 2006 Federal regulations allow three options: (1) a severe discrepancy between intellectual ability and achievement, (2) a process based on the child’s response to scientific, research-based intervention, and (3) other alternative research-based procedures. The third option allows the use of a “pattern of strengths and weaknesses” (PSW) in SLD determination. The practice involves using assessment data to document a PSW in cognitive abilities and/or achievement. Because the third option is a federal mandate, states must allow PSW. Most states have specific criteria for using PSW in SLD identification. Even in states that indicate a preference for PSW, local school districts are allowed to decide which SLD identification method they will use.
What are the main PSW methods?
There are several PSW methods. Each method includes criteria for evaluating cognitive and academic performance that, when met, indicate a PSW in scores that is consistent with SLD. Although the conceptual definition of PSW is agreed upon by all authors of PSW methods, the criteria and methods vary. Here are four leading methods of PSW:
- The Discrepancy/Consistency Method (DCM) is based on a systematic examination of cognitive and academic achievement test scores. The DCM is conceptual and could be used with any measure of psychological processes but has been associated with the PASS (Planning, Attention, Simultaneous, Successive) theory (https://jacknaglieri.com/).
- The Dual Discrepancy/Consistency (DD/C) method is based on the most salient diagnostic markers of SLD that have been prevalent in the literature for decades. DD/C is grounded in the Cattell-Horn-Carroll (CHC) theory and important neuropsychological functions (Flanagan, D. P., Ortiz, S. O., & Alfonso, V. C., 2017).
- Dehn’s PSW model uses software known as The Psychological Processing Analyzer (PPA) to analyze standardized test scores for statistically significant strengths and weaknesses among 14 neuropsychological (cognitive) processes and among 8 areas of achievement (Essentials of Processing Assessment 3rd Edition (schoolhouseeducationalservices.com).
- The Core-Selective Evaluation Process (C-SEP) is a focused and data-driven assessment and analysis method informed by contemporary cognitive theory and driven by clinical judgment. This is method is more informal than most PSW methods and it is mainlyused in the state of Texas (https://csep.online/index.html).
What are the main PSW criteria for SLD identification?
The figure below illustrates the primary PSW criteria and PSW analysis of test scores across the different PSW models. The bottom left oval represents cognitive processing weaknesses, and the bottom right oval represents academic skill weaknesses. The double-headed arrow between the two bottom ovals indicates a statistical equivalency between academic and cognitive deficits (referred to as “consistency”). The double-headed arrows between the top oval and the two bottom ovals indicate a statistically significant difference between cognitive ability/processing strengths/academic strengths and areas of cognitive (bottom left oval) and academic (bottom right oval) weaknesses. To qualify for SLD under PSW, a student should have: (1) a least one intra-individual (within person) weakness in cognitive processes; (2) at least one strength in cognitive processes; (3) low achievement in at least one academic area; (4)
consistency between the low achievement area and related weak cognitive process(es); (5) and, also a strength and weakness within the achievement areas.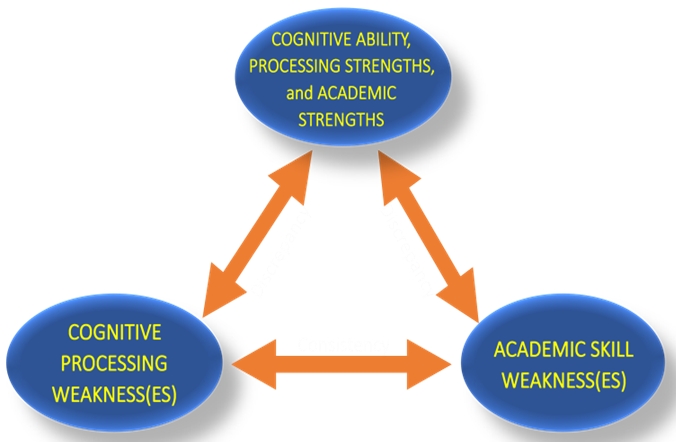
What is the evidence in support of PSW?
PSW methods assume that one or more cognitive processing weaknesses underlie SLD. The occurrence of significant cognitive processing weaknesses in a child who displays otherwise normal cognitive abilities is viewed as a strong indication of SLD. The evidence-base for this claim is extensive. A meta-analysis of 32 studies by Johnson, Humphrey, Mellard, Woods, and Swanson (2010) found “moderately large to large effect sizes in cognitive processing differences between groups of students with SLD and typically achieving students.” In this review, the cognitive processing weaknesses identified in SLD populations were working memory, short-term memory, phonological processing, processing speed, executive function, and language.In another review of the literature, Hale, Chen, Tan, Poon, and Fitzer (2016) concluded that “children with disabilities have varying deficits in attention, phonological, orthographic, rapid naming, long-term memory, memory encoding/retrieval, fluid reasoning, spatial processing, receptive/expressive language, psychomotor skills, response inhibition, working memory, processing speed, and executive function relative to typical children.”
What are some advantages of using PSW to identify students with SLD?
- It helps teachers and parents understand why the student has academic learning difficulties.
- It helps everyone better understand the student’s cognitive strengths and weaknesses.
- It allows earlier identification of students with SLD compared to other methods.
- It is based on theory and is used to inform intervention design and selection, as well as differentiated instruction.
- SLD placement decisions are based on reliable and valid measures of cognitive abilities and processes.
- It provides structure for analyzing multi-battery test score data.
- It is legally defensible.
More resources on Patterns of Strengths and Weaknesses (PSW):
Essentials of Processing Assessment 3rd Edition (This is a book about PSW.)
The Psychological Processing Analyzer (This is PSW software based on Dehn’s model.)
Using the Pattern of Strengths and Weaknesses Method to Identify Specific Learning Disabilities (4-page laminated, reference guide on PSW.)
